BRUNO MIROUX
Principal Investigator
INSERM RESEARCH DIRECTOR
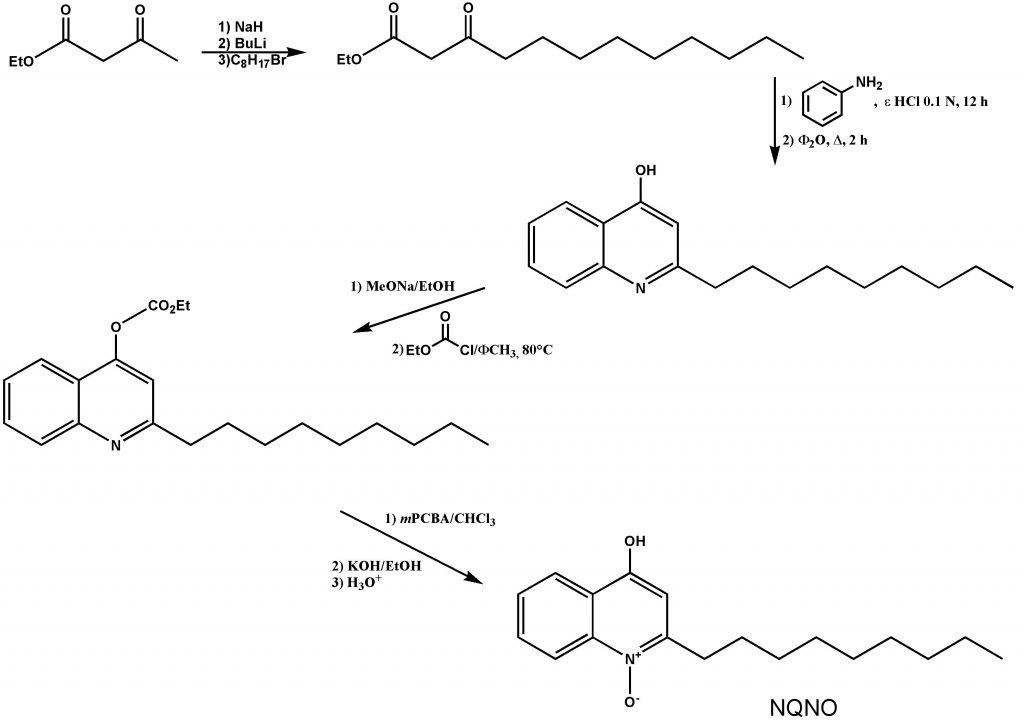
One of our recurrent works is the development and/or the synthesis of some derivatives involved in affinity mechanism with certain proteins. Those derivatives are called ligands and may act following the case, as a protein inhibitor or a protein activator. Two interesting examples are given here concerning the synthesis of tridecylstigmateline (TDS) (see Fig. 1) and 4-hydroxynonylquinoleyl-N-oxyde (NQNO) (see Fig. 2) which are two cytochrome b6f inhibitors commonly used in order to chock the cytochrome structure prior crystallization (see [1-2] as example of application).
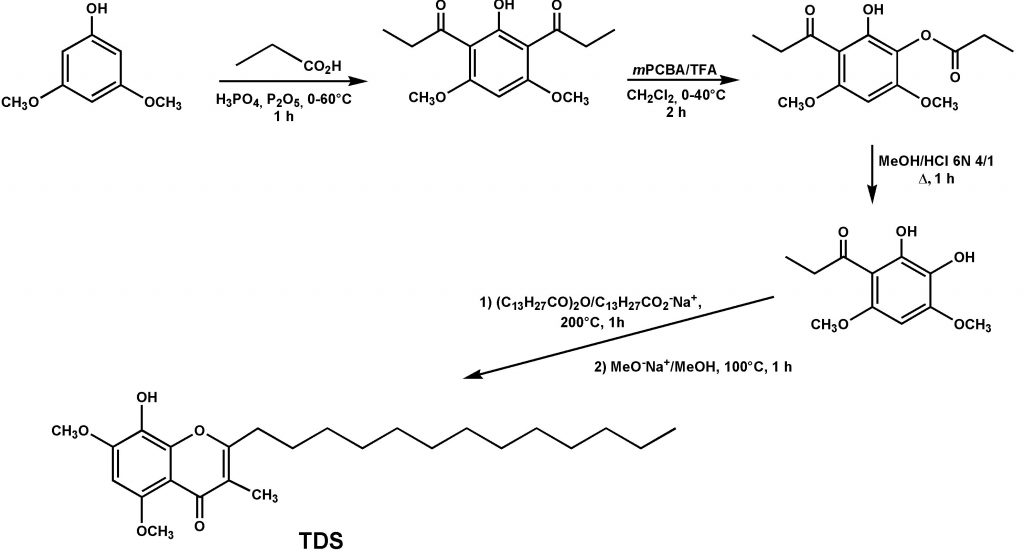
Figure 1. synthetic pathway for TDS according to Höfle et al. [3]