
Martin
Picard
Research Director

Valérie
Biou
Researcher

Laurent J.
Catoire
Research Director

Céline
Madigou
Enginneer

Alexis
Lodé
Post-doc

Marine
Novelli
pHD STUDENT
Background
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria are now ubiquitous in both hospital settings and the larger community and pose a threat to future clinical management of disease. Efflux systems play a central role as their expression can raise antibiotic resistance by several orders of magnitude, rendering some antibiotics clinically useless.
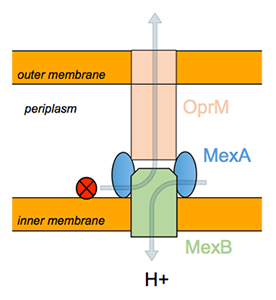
In the Gram negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, efflux transporters are organized as tripartite systems where MexB, the RND pump (member of the Resistance, Nodulation, cell Division family) located in the inner membrane works in conjunction with MexA, a membrane fusion periplasmic protein, and OprM, an outer membrane channel.
The cytoplasmic inner membrane protein acts as an energy-dependent pump with broad substrate specificity.
Methodology
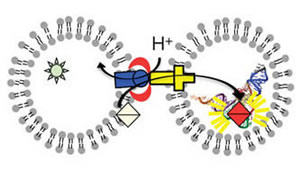
The structural study of efflux pumps from E. coli and P. aeruginosa allows a description of transport mechanisms with atomic resolution but biochemical data on purified proteins is essential to draw a picture of the dynamical features and of the couplings between the components. To that end, we have developed an original system using proteoliposomes to study the assembly state and the transport activity of efflux pumps.
Objectives
The dynamical basis for multidrug recognition and transport is investigated in a quantitative way. In addition, using a bottom-up approach, we are deciphering the factors that have been postulated to be additional players and regulators of the transport. Finally, this project opens towards technological developments, namely the miniaturization of the system to eventually allow for the screening of efflux pump inhibitors.
Bibliography:
- Verchère A, Dezi M, Adrien V, Broutin I, Picard M. In vitro transport activity of the fully assembled MexAB-OprM efflux pump from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature Communications (2015); 6:6890.(Pubmed)
- Ntsogo Enguéné VY, Verchère A, Phan G, Broutin I, Picard M. Catch me if you can: a biotinylated proteoliposome affinity assay for the investigation of assembly of the MexA-MexB-OprM efflux pump from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Frontiers in Microbiology (2015); 6.(Pubmed)
- Daury L, Orange F, Taveau J-C, Verchère A, Monlezun L, et al. Tripartite assembly of RND multidrug efflux pumps. Nature Communications. (2016) ; 7: 10731.(Pubmed)